The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) stands as a monumental piece of legislation in the sphere of civil rights, aimed at ensuring that individuals with disabilities are granted the same opportunities and rights as those without. Enacted in 1990, the ADA has led to significant changes across various industries, ultimately fostering environments that are more inclusive and accessible. The essence of the ADA is to eliminate barriers that impede the full participation of disabled individuals in public life, and it encompasses a wide array of entities, from government facilities to private businesses, including the hospitality industry.
The hospitality industry, comprising hotels, restaurants, and other lodging and dining establishments, plays a crucial role in society by providing essential services for both locals and travelers. Given the diversity of clientele these businesses serve, it becomes imperative for them to meet ADA compliance standards to ensure that individuals with disabilities can partake in their services without limitations. This article delves into the various aspects of ADA compliance within the hospitality industry, highlighting key areas such as entrance accessibility, guest accommodations, dining areas, and employee rights. By exploring these focus areas, we aim to present a comprehensive understanding of how the ADA shapes the hospitality sector and the benefits it brings to everyone involved.
Entrance and Facility Accessibility
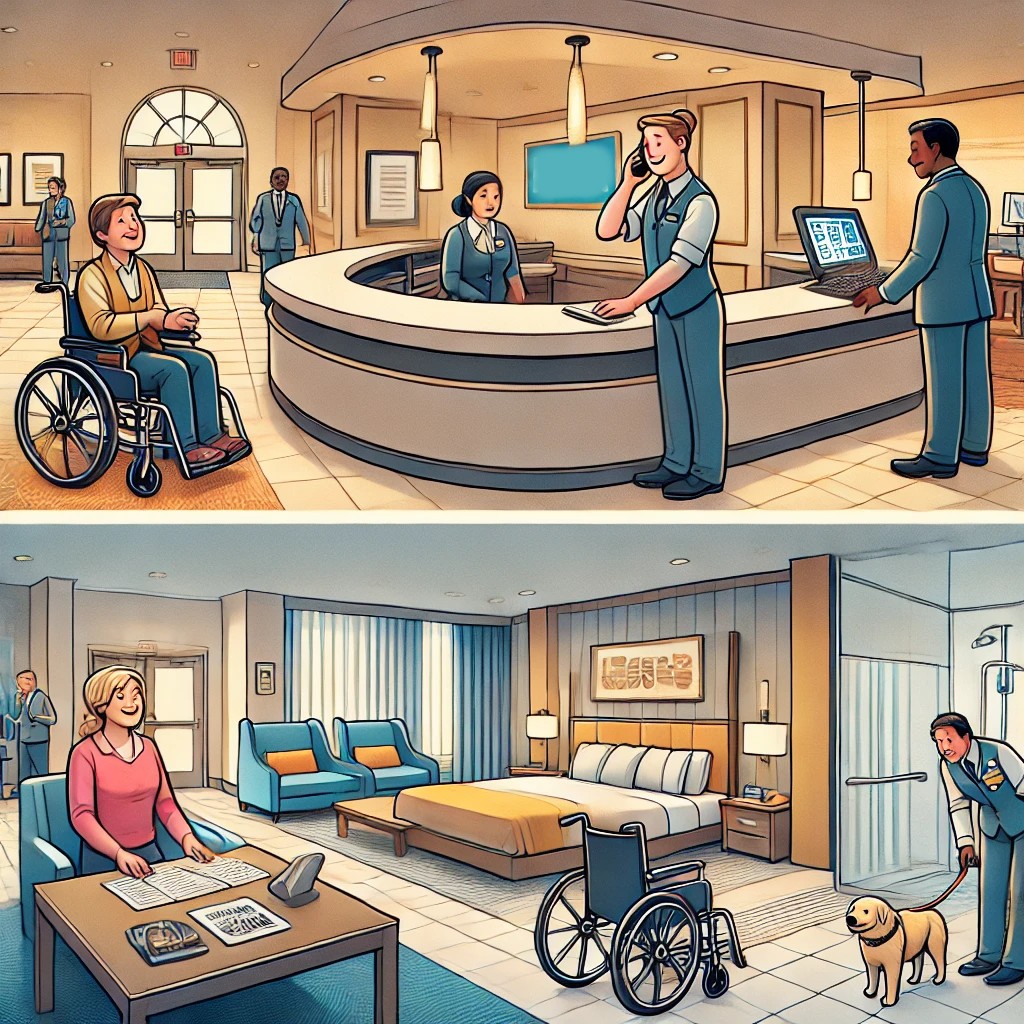
One of the most visible aspects of ADA compliance in the hospitality industry is the accessibility of entrances and overall facilities. For a hotel or restaurant to be considered compliant, its entryways and public spaces must be accessible to individuals with disabilities, which often involves structural modifications. Ramps, automatic doors, and well-marked pathways are some of the common features that establishments must integrate to ensure barrier-free entry for all patrons.
The importance of accessible entrances cannot be overstated. It is the first point of contact that a guest has with the establishment, and as such, it sets the tone for the entire experience. Ensuring that paths are clear of obstacles and providing adequate signage are essential steps in creating an inviting environment. Additionally, according to the ADA Standards for Accessible Design, doorways must be wide enough to accommodate wheelchairs, and there must be a level ground outside and inside the entrance to facilitate smooth movement.
Within the facility, key areas like reception desks and common spaces should also be designed with accessibility in mind. Lowered counters at check-in areas, elevators with braille buttons and audible signals, and tactile flooring indicators are just a few examples of how hospitality venues can cater to the needs of disabled guests. By taking these measures, businesses not only comply with the ADA but also foster an inclusive atmosphere that can enhance their reputation and customer satisfaction.
Guest Room Accommodations
When it comes to guest room accommodations, hospitality establishments have specific requirements to meet under the ADA. Hotels and motels must offer a certain number of rooms that are readily accessible to individuals with disabilities. This includes the provision of features such as wide doorways, roll-in showers, grab bars, and lower fixtures to ensure ease of use for guests with varying needs.
Moreover, the ADA mandates that accessible rooms should be distributed among different classes and types of lodging available at the establishment, including luxury suites, standard rooms, and budget accommodations. This regulation is designed to ensure that individuals with disabilities have diverse options to choose from, just like any other guest.
Additionally, reservation systems must provide the same level of detail about the accessible features of the rooms as they do for other rooms. This means that guests with disabilities should be able to make reservations for accessible rooms with the assurance that the room will meet their needs when they arrive. Facilities must also ensure that staff are trained to understand and address accessibility-related inquiries, further enhancing the guest experience.
Restaurant and Dining Area Accessibility
Restaurants within the hospitality industry are also subject to ADA regulations, particularly concerning dining area accessibility. For a dining experience to be genuinely inclusive, restaurants must ensure that seating arrangements and dining facilities are accessible to individuals with disabilities. This often involves strategically placing tables to allow enough space for wheelchair maneuverability and ensuring that pathways are unobstructed.
Accessible dining additionally means providing menus in accessible formats, such as braille or large print, and offering assistive listening devices for guests with hearing impairments. The layout of buffets and self-service areas must also take into account the needs of disabled patrons, ensuring that counters are of a suitable height and that items can be easily reached without assistance.
Furthermore, restroom facilities within dining establishments must adhere to strict ADA guidelines. This includes providing at least one accessible stall in each restroom, with features like grab bars, lower sinks, and automatic door openers. Compliance in these areas ensures that all guests can dine with dignity, comfort, and independence, significantly enhancing their dining experience.
Employee Rights and Work Environment
Beyond accommodating guests, the ADA also outlines requirements for the treatment of employees with disabilities within the hospitality industry. Employers are mandated to provide reasonable accommodations to qualified employees with disabilities unless doing so would cause undue hardship. These accommodations can range from modified work schedules and job restructuring to physical adjustments, like ergonomic workstations and accessible break rooms.
Reasonable accommodations are fundamental in ensuring that individuals with disabilities are given equal opportunities to contribute to the workforce. Employers must also ensure that the hiring process is accessible, which includes making job applications available in accessible formats and conducting interviews in accessible locations.
It’s also critical for hospitality employers to foster an inclusive culture by providing regular training and education on disability awareness and the rights of disabled employees. Such training helps prevent discrimination and promotes understanding among staff, creating a more supportive and productive work environment.
Moreover, the ADA protects employees from retaliation if they exercise their rights under the Act. This means that employees who request accommodations or report non-compliance issues cannot be subjected to adverse employment actions, such as demotion or termination, as a result of their advocacy. By adhering to these guidelines, hospitality employers can significantly enhance workplace diversity and inclusion.
The Economic Benefits of ADA Compliance
While ADA compliance is fundamentally about civil rights and social inclusion, it also brings considerable economic benefits to the hospitality industry. By making facilities accessible, businesses can tap into a larger customer base. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, nearly 61 million adults in the United States live with a disability. By ensuring that their services are accessible, hospitality businesses can attract and retain these potential customers, thereby boosting their bottom line.
Additionally, accessible facilities often receive positive reviews and word-of-mouth recommendations, enhancing a business’s reputation and customer loyalty. Guests who have positive experiences due to ADA-compliant features are more likely to return and recommend the establishment to others, thus providing a competitive edge.
Moreover, compliance can lead to financial incentives. Various federal and state programs offer tax credits and deductions to businesses that make accessibility improvements. These financial benefits can offset some of the costs associated with implementing ADA-compliant features, making it a financially sound decision as well.
Non-compliance, on the other hand, can result in legal repercussions, including costly lawsuits and penalties. Therefore, investing in ADA compliance is not only a moral and ethical obligation but also a sound business strategy that can lead to long-term financial gains and stability.
Conclusion
The Americans with Disabilities Act has profoundly impacted the hospitality industry by fostering environments that cater to the needs of all individuals, regardless of their physical or mental abilities. From ensuring accessible entrances and facilities to providing suitable accommodations and upholding employee rights, compliance with ADA standards is crucial in creating an inclusive and welcoming atmosphere.
The benefits of ADA compliance extend beyond meeting legal requirements. By embracing accessibility, hospitality businesses can tap into a broader customer base, enhance their reputation, and enjoy financial incentives. Moreover, fostering an inclusive culture and workplace can lead to higher employee satisfaction and productivity, further contributing to the overall success of the business.
Ultimately, ADA compliance is about recognizing and valuing the dignity of every individual. By adhering to these standards, the hospitality industry not only complies with the law but also upholds the principles of equality and inclusivity, benefiting both their customers and their business.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What does ADA Compliance mean for the hospitality industry?
ADA Compliance in the hospitality industry signifies that businesses such as hotels, restaurants, and other venues are required to ensure their facilities are accessible to individuals with disabilities. This encompasses physical accessibility which means providing ramps, elevators, and wide doorways, as well as offering aids for those with visual or hearing impairments, like braille menus or closed captioning for TVs. It’s not just about physical requirements; it also involves ensuring equal access to services and accommodations, ensuring communication is as effective with individuals with disabilities as it is with others. ADA compliance leads to a holistic inclusion of all individuals, showing respect and equal opportunity, and ultimately expanding the customer base by being inclusive to all guests.
2. Are there specific areas in a hotel that must adhere to ADA Standards?
Yes, there are specific areas in hotels that must be compliant with ADA standards. These areas include guest rooms, which must have a certain percentage of rooms accessible to people with disabilities, inclusive of features like roll-in showers, turning space for wheelchairs, and amenities placed at convenient levels. Public spaces such as the lobby, swimming pool, fitness center, restaurants, parking areas, and conference rooms also need to have accessible routes and features, such as ramps, lift systems. Additionally, elements like tactile indicators for people with visual impairments, audible and visible alarms, signs with appropriate contrast and braille, need to be there. Ensuring these accommodations are not just about ticking checkboxes; it’s about providing an environment where everyone feels welcomed and can enjoy the amenities equally.
3. How does ADA compliance impact the design and architecture in the hospitality industry?
The ADA has a significant impact on design and architecture, aiming to create spaces where accessibility is seamlessly integrated rather than being an afterthought. Architects and interior designers need to incorporate these standards from the initial stages of design. This covers ensuring wide passageways, appropriate counter heights, non-slip floors, lever handles on doors instead of knobs, and softly graded ramps. This design focus extends beyond just the main entry areas and impacts bathrooms, ensuring toilets, showers, and sinks are usable by everyone. The challenge is to make these elements blend stylishly with the venue’s overall aesthetic so that functionality meets style. By doing so, environments are not just compliant, but they are truly welcoming to guests of all abilities.
4. What are the penalties for not complying with ADA standards in the hospitality industry?
Failing to comply with the ADA standards can result in significant penalties for businesses in the hospitality industry. Penalties can include fines, which may range significantly based on the severity of non-compliance and whether it’s a first-time or repeated violation. Beyond fines, non-compliance can lead to lawsuits, which can bring additional financial burdens and damage to the company’s reputation. It’s also about the physical and social costs; not being accessible means losing customers and creating environments that exclude potential guests. Therefore, meeting ADA compliance is not only a regulatory requirement but also a smart business strategy to expand market reach and enhance customer satisfaction. Being proactive and seeking expert assessments can help businesses mitigate these risks.
5. What are some examples of how hotels and restaurants can improve ADA compliance?
Hotels and restaurants can take numerous steps to improve ADA compliance and offer a better experience for all guests. For hotels, updating rooms to include accessible bathrooms with lowered fixtures and standing showers, installing visual and auditory fire alarms, and providing room options with features like beds on adjustable frames can be beneficial. For restaurants, ensuring tables are spaced with enough room for a wheelchair to move comfortably, offering menus in braille or large print, and having personnel trained in communicating with guests with disabilities, like using sign language, improve accessibility significantly. It’s also effective to engage in regular audits of accessibility features and staff training to maintain adaptations. Establishments may also use technology, allowing guests to easily express specific accommodation needs when booking, which can preemptively solve many potential issues. Making these inclusions a natural standard of service reflects a commitment to inclusivity and equality.






